First we establish that the universe had a beginning and was created by a transcendent first-cause - God. We observe that the process of creation, based on cosmological findings over the last 100 years, is consistent with the biblical record in Genesis. This is evidenced by the Big-Bang event where space, time and matter came into existence simultaneously.
Based on credible scientific evidence from many approved sources, scientists have confirmed that the universe had a beginning. Since SOMETHING cannot be created from NOTHING, there must have been a cause outside of the universe responsible for the creation of the universe. This outside cause is referred to as the Transcendent First Cause.
This conclusion is supported by the following truth claims.
Summary: The claim that the universe had a beginning is founded on credible, empirical evidence. Due to the overwhelming amount of evidence, many consider this claim the final word in cosmology [REF-PUR01].
This claim is supported by the following evidence.
Summary: The Second Law of Thermodynamics states that the fixed amount of energy in the universe will disperse over time. Another way to understand this is that the order the things we see around us is unraveling and the universe is trending toward disorder. Because of the dispersion of energy over time, life as we know it will cease to exist. Because we are still in a state of orderliness, time must be finite, not infinite. Otherwise, we would have already reached the final state of complete disorder. Therefore, the universe must have had a beginning.

Thermodynamics is the study of heat and energy. It is comprised of three laws that describe the relationships between all forms of energy. Most notable is the Second Law of Thermodynamics which is credited to the French scientist Sadi Carnot in 1824.
The Second Law of Thermodynamics states that matter is becoming more disordered and that the fixed amount of energy in the universe is becoming more dispersed over time.
Another way to understand the Second Law of Thermodynamics is that the order the things we see around us is unraveling and becoming less structured.
A word picture that illustrates this process is the unraveling of knit garment. If we pull on a loose end of thread, we can unravel the entire garment until it no longer resembles the original. Consequently, the effort required to knit the original garment is undone.
Another example of this process is the burning of wood. The burning process transforms the original wood, cellulose (C6H10O5) into new forms of energy such as heat, light, atomic elements such as carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O), and other non-flammable elements such as ash and soot. During this burning process, no new energy is gained, and none is lost. Energy in the form of heat is dispersed from the burning wood to the surrounding environment.
In both of these examples, the garment and wood lose form and structure.
Because our universe is a closed system where no new energy is being fed into it, the amount of energy in the universe is constant or fixed. This implies that the energy in the universe is conserved. This is the First Law of Thermodynamics.
According to the Second Law of Thermodynamics, both the entropy (disorder) and enthalpy (heat) of the universe will increase over time.
Ultimately, the universe will become a featureless soup in which no life is possible. Given enough time, the universe will inevitably stagnate in what scientists refer to as a state of heat death. Once the universe reaches this state, no further change is possible. The universe will be in a final state of equilibrium.
So why is this relevant to the universe's beginning?
This discovery unmistakably demonstrates the irreversible passage of time and state of the universe. The universe is progressively moving from a state of orderliness, toward a final state of disorder or heat death. Therefore, we conclude that the universe must have had a beginning.
We also conclude that time is finite not infinite. For if time were infinite, we would already be in the final state of heat death [MATH-IS04].
Resources:
Summary: Einstein's General Theory of Relativity demonstrated that time, space, and matter are inter-dependent. Essentially, they all came into existence simultaneously. This means that time could not have existed before matter and space. This disproves theories claiming that time existed before space and matter, dispelling the need for a transcendent first-cause.

Einstein's General Theory of Relativity (circa 1917) was intended to be a new theory of gravity. It supersedes Newton's law of universal gravity established in 1687.
Einstein's theory demonstrated that time, space, and matter are inter-dependent thus the name "relativity". In fact, they all came into existence simultaneously and are therefore coexistent. This means that one cannot exist apart from the other two.
Over the last 100 years, Einstein's General Theory of Relativity has been calibrated and validated. Cosmologists confirm that Einstein's theory accurately reflects the origin of time, space, and matter.
Einstein referred to his discovery "irritating". Because Einstein was a pantheist, he wanted the universe to be self-existent - not reliant on an outside cause - even though the universe appeared to be one big effect with a first cause.
Subsequently, Einstein introduced a fudge factor called the cosmological constant into his equations in order to show that the universe was static and devoid of a singularity beginning.
In 1919, Arthur Eddington determined the universe was not static and had a beginning. He concluded that Einstein's original General Theory of Relativity was true except for the cosmological constant introduced by Einstein [COS-EV05].
Sir Arthur Eddington wrote
"Philosophically, the notion of a beginning of the present order of Nature is repugnant to him. I would rather be inclined to think that the present state of quantum theory suggests a beginning of the world very different from the present order of Nature. Thermodynamical principles from the point of view of quantum theory may be stated as follows: (1) Energy of constant total amount is distributed in discrete quanta. (2) The number of distinct quanta is ever increasing. If we go back in the course of time, we must find fewer and fewer quanta, until we find all the energy of the universe packed in a few or even in a unique quantum." [REF-EDD01]
Einstein eventually concurred with Eddington's findings.
Einstein's General Theory of Relativity demonstrates that the universe had a beginning and was not self-existent. His model converges onto a singular event whereby time, space, and matter came into existence simultaneously.
More importantly, Einstein's theory disproves all other theories claiming that time existed before space and matter, dispelling the need for a transcendent first-cause.
Today, cosmologists agree that the universe comprised of time, space, and matter had a singularity beginning which is not explainable by nature means.
Resources:
Summary: Alexander Friedman and Georges LeMaître were the first to develop models of an expanding universe with a singularity beginning. Their models later became known as the Big Bang model.

During the 1920s the Russian mathematician Alexander Friedman and the Belgian astronomer Georges LeMaître decided to take Einstein’s original equations from the General Theory of Relativity at face value. As a result, they came up independently with models of an expanding universe. They, like Sir Arthur Eddington, exposed Einstein's fudge factor.
The Friedman-LeMaître model eventually came to be known as the Big Bang theory. Their model predicts an absolute beginning of our expanding universe. It traces the expansion of the universe back in time to a singular point of origin.
Using the Friedman-LeMaître model, everything gets closer and closer together as we go back in time. The envelope of space gets smaller and smaller. Eventually, space and time converge onto a singular point of origin. At that point we reach the space-time boundary.
The space-time continuum can be represented geometrically as a cone. What is significant about this is that while a cone can be extended indefinitely in one direction (upward), it has a boundary point in the other direction (downward). Because this vertical direction represents time and the boundary point lies in the past, the model implies that past time is finite and had a beginning.

Because space is the arena in which all matter and energy exist, the beginning of space-time is also the beginning of all matter and energy. It is the beginning of the universe.
Like Einstein, Friedman and LeMaître concluded that space, time, and matter were all created simultaneously and are inter-dependent. Moreover, Friedman and LeMaître demonstrated that because the universe is continually expanding, it must have had a singular point of origin.
Resources:
Summary: Edwin Hubble discovered that the light from distant galaxies appeared to be redder than expected. He also discovered that the red shift increased in direct proportion to the distance the galaxies were located away from the cosmic explosion. He concluded that this red shift was due to the stretching of the light waves as the outermost galaxies move away from us. His findings proved that the universe is expanding from a singularity beginning.

In 1929, the American astronomer Edwin Hubble, through tireless observations at Mt. Wilson Observatory, made a startling discovery which verified Friedman and LeMaître’s theory of an expanding universe [COS-EV03].
Hubble found that the light from distant galaxies appeared to be redder than expected. This red shift in the light was due to the stretching of the light waves as the outtermost galaxies move further away from the original cosmic explosion. Hubble further discovered that the red shift increased in direct proportion to the distance the galaxies were located away from the cosmic explosion.
Hubble's discovery was proof that the physical boundaries of space were expanding, not just that the planetary bodies in space that were simply moving further apart into an infinitely large, preexisting physical space.
Hubble's discovery became known as the Hubble's Law. Hubble's Law states that the greater the distance between any two galaxies, the greater their relative speed of separation, and thus red shift.
The Hubble's Law was further advanced in the 1990's when the Hubble Space Telescope and NASA's WMAP spacecraft were used to measure other critical factors that further conformed the Big Bang theory.
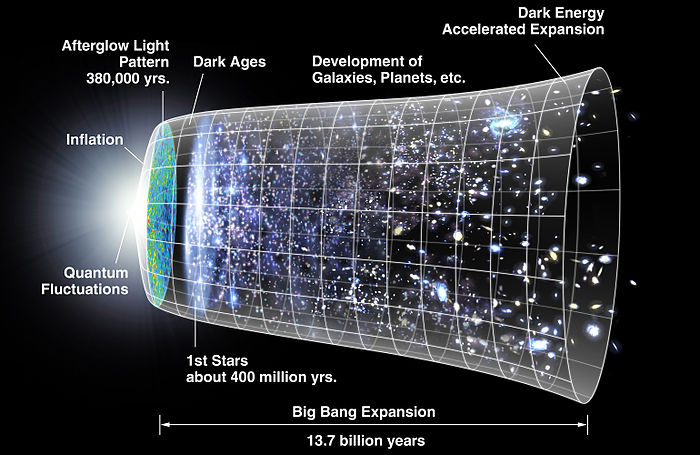
Together with the Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation (CMBR) discovery [COS-EV10], Hubble's Law represents the best available evidence for the Big Bang theory. CMBR bears witness to an enormous explosion, while Hubble's red shift bears witness to the expansion of the space boundaries in the universe.
Resources:
Summary: Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson accidentally discovered Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation (CMBR) left over from the Big Bang. The afterglow of the background radiation observed by Penzias and Wilson was actually light and heat from the initial explosion.

In 1964, Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson discovered Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation (CMBR) left over from the Big Bang. Penzias and Wilson believed in the Big Bang theory, which states that the universe was created in a massive explosion-like event 13.72 billion of years ago.
The discovery of CMBR was a major development in modern cosmology. Although predicted by earlier theoretical work around 1950, it was first discovered accidentally by American radio astronomers Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson as they experimented with the Holmdel horn antenna at Bell Labs. The discovery was important evidence for an explosion that set the universe in motion.
The afterglow observed by Penzias and Wilson was actually light and heat from the initial explosion. The light is no longer visible because the wavelengths were stretched by the expanding universe [COS-EV02].
Independently, Robert H. Dicke, Jim Peebles, and David Wilkinson, astrophysicists at Princeton University, were preparing to search for microwave radiation in this region of the spectrum. Dicke and his colleagues reasoned that the Big Bang must have scattered not only matter that condensed into galaxies, but also must have released a tremendous blast of radiation.
Measurements of the CMBR have made the inflationary Big Bang theory the standard model of Cosmology [REF-SCT01]. The discovery of the CMBR in the mid-1960s curtailed any interest in alternative theories such as the Steady State Theory [REF-PUR01] [REF-SSM01].
CMBR was proof positive that the universe began with a massive explosion.
Resources:
Summary: Scientists observed cosmic ripples - slight variations in temperature - that enabled matter over time to coalesce by gravitations attractions into galaxies. This coalescing of matter into galaxies is referred to as the Great Galaxy Seeds of the universe. This property of coalescence was so well regulated that it was not too great to ensure the universe did not collapse upon itself and not too small to ensure that matter in the universe did not become infinitely dispersed.

Scientists observed that there was slight variation in the temperature of the Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation (CMBR) discovered by Penzias and Wilson. These temperature variations or cosmic ripples enabled matter to coalesce by gravitational attractions into galaxies over time.
This coalescing of matter into galaxies was observed by the NASA Cosmic Background Explorer (COBE) satellite in 1992. Two of COBE's principal investigators, George Smoot, and John Mather, received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2006 for their discovery.
The COBE Differential Microwave Radiometers (DMR) experiment was designed to search for primeval fluctuations in the brightness of the CMBR representing small temperature differences between different parts of the sky.
The primeval fluctuations were observed to be extremely faint, only one part in 100,000. The fluctuations represent the varying densities of matter in the early universe. These densities were referred to as galaxy seeds.
These galaxy seeds are believed to have given rise to the structures that populate the universe today, specifically, clusters of galaxies and vast regions devoid of galaxies. This discovery was aptly coined the Great Galaxy Seeds of the universe.
These density ripples of matter from billions of years ago can be seen in the NASA image below.
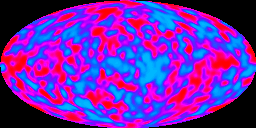
Scientists also observed that the expansion of the universe was highly regulated causing matter to coalesce into galaxies. In fact, this property of coalescence was so well regulated that it was not too great to ensure the universe did not collapse upon itself, and not too small to ensure that matter in the universe did not become infinitely dispersed [COS-EV16].
From the COBE data we can readily observe that the densities of matter or forming galaxies of long ago are quite different from the galaxies we observe today. We can conclude that the structure of the universe has changed over time. This change in structure is further proof of our expanding, fine-tuned universe.
Resources:
Summary: The universe is not self-existent. It did not exist from eternity past but had a beginning a finite time ago. In 2003, Arvind Borde, Alan Guth and Alexander Vilenkin were the first to develop a mathematical proof that described the universe as not having an infinite past, but rather, a singularity beginning.

In 2003, mathematician Arvind Borde, and physicists Alan Guth and Alexander Vilenkin were able to prove mathematically that any universe which has been expanding throughout its history did not exist from eternity past but had a past space-time boundary.
What makes their proof so powerful is that it holds so long as time and causality hold. Their theory does not rely of any other physical factors present in the early universe. It is independent of the theory of gravitation as defined by Einstein which relies on the presence of mass and gravity.
The Borde-Guth-Vilenkin theorem is yet another demonstration that the universe had a beginning. Their approach was unique from Einstein's theory, and Friedman and Georges LeMaître's model of the universe. Taken together, these three approaches reinforce the theory of a past space-time boundary.
Resources:
The claim that the universe had a beginning is founded on credible, empirical evidence from a largely secular scientific community. This evidence covers a broad range of cosmological areas including cosmic background radiation, energy dispersion and conservation, and residual light waves.
The discoveries of the late 19th and 20th centuries demonstrate that the universe has a singularity beginning. These discoveries are depicted in the following timeline.

The following is a summary of the key evidence.
This singularity beginning of time, space, and matter is described in the book of Genesis.
In the beginning God created the heavens and the earth (Genesis 1:1).
In other words, at the beginning of time God created space and matter. In the book of Hebrews, the author makes clear that God supernaturally created time, space, and matter out of nothing.
By faith we understand that the universe was created by the word of God, so that what is seen was not made out of things that are visible. (Hebrews 11:3 ESV)
This expansion of the universe is described in the book of Psalms.
You stretch out the starry curtain of the heavens. (Psalm 104:2)
Expansion is likened to stretching the starry curtain or outer boundary of space, much like stretching the skin of a balloon as it is inflated.
This fine tuning of the universe is described in the book of Psalms.
This is what the Lord says: I would no more reject my people than I would change my laws that govern night and day, earth and sky. (Psalm 104:2)
This passage make it clear that God instituted physical laws that govern and sustain the universe. It also states that these laws are constant and immutable, as are the promises God made to the nation of Israel.
Most notable is the relationship between the Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation (CMBR) and the Hubble cosmological Red Shift Distance discoveries [COS-EV10] [COS-EV02]. Taken together, these discoveries are regarded as the best available evidence for the Big Bang theory. CMBR bears witness to the remnant radiation of a dense and hot phase in the early universe. Red shift bears witness to the expansion of the space boundaries in the universe..
Measurements of the CMBR have made the Inflationary Big Bang theory the standard model of cosmology in most scientific circles [REF-SCT01]. This further curtailed any interest in alternative theories such as the Steady State Theory [REF-PUR01] [REF-SSM01].
Collectively, this evidence demonstrates unequivocally that the universe had a singularity beginning where time, space and matter came into being simultaneously.
Einstein's law, Friedman-LeMaître's Big Bang model, and Borde-Guth-Vilenkin's mathematical theorem demonstrate a singularity beginning of time. Penzias-Wilson's discovery of Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation, the discovery Great Galaxy Seeds of the universe, and Hubble's law demonstrate a singularity beginning of space. Finally, the Second Law of Thermodynamics demonstrates a singularity beginning of matter.
Resources:
Summary: Mathematicians have long argued that an actual infinity cannot exist. Infinity is a concept. It serves as a potential limit which is never reached. Essentially, it is merely a figment of human imagination, not reality.

Infinity is perhaps the most misunderstood concept. Many regard infinity as reality.
While infinity is a useful theoretical tool used in the field of Mathematics to understand infinite sets of objects and estimate a convergent series of numbers, it is not observed as a factual reality in the material world comprised of time, space and matter. It is merely a figment of human imagination.
What are the implications of an infinity past as it relates to creation?
Infinity has been used to justify a number of cosmological theories, most notably the multiverse (multiple universes) and a self-existent universe. These concepts were first espoused in the mid 1500's by Thomas Diggies and Giordano Bruno [REF-INF01]. They postulated that there were an infinite number of universes and planets, unbounded space, and so on. In the absence of scientific evidence, their concepts were assumed to be plausible.
Infinity has also been used to justify the theory of evolution in the mid 1800's. The implication was that "given enough time", evolving genetic traits would prove viable and freely propagate to future generations. Unfortunately, these suppositions are not evinced by the fossil records nor the findings of modern biological research.
In his book Reasonable Faith [REF-WLC03], William Lane Craig argues,
"A potential infinity can exist, but an actual infinity cannot exist. … For if an actual infinity could exist, this would spawn all sorts of absurdities."
These absurdities result from a tension between a theoretical infinity and the finiteness of creation itself. They also contradict the laws of logic, most notably, the Law of Causality [PHY-IS01] and Law of Contradiction [PHY-IS02].
In order for an actual infinity past to exist, the past must be comprised of an infinite numbers of events. This implies that the universe did not have a beginning, and that the universe has been in a steady state of cause and effect forever. Using simple logic, this premise can be refuted by the following absurdities:
The implausibility of an actual infinity past is best illustrated by the paradox of the Grand Hotel developed by the German mathematician David Hilbert [REF-HIL01]. Imagine that Hilbert's Hotel is full and yet can accommodate an infinite number of new guests. This implies Hilbert's Hotel must have an infinite number of rooms. The marquee on the hotel would read "NO VACANCIES, GUESTS WELCOME". Because of the Law of Non-Contradiction [PHY-IS02], Hilbert’s Hotel can’t be infinitely full and infinitely empty at the same time.
The illustration of Hilbert's Hotel becomes even more absurd if it has a finite number of rooms. It is impossible for Hilbert's Hotel to accommodate an infinite number of guests past, present, and future when it only has a finite number of rooms. Essentially, anything that is finite cannot be simultaneously infinite [PHY-IS02].
Because the universe has been proven by modern science to be bounded in terms of time, space and matter, infinity past cannot exist.
Resources:
Summary: The Law of Causality states that something cannot be created from nothing. In fact, we have not observed any instance when something occurred without a precipitating cause.

The Law of Causality has garnered much attention over the millennia. It is considered one of the most fundamental laws of the universe.
As it relates to Apologetics, the Law of Causality states that something cannot be created from nothing.
The Law of Causality is rooted in the fundamental law of physics [REF-CAU01]. In the physical world, both energy and momentum are conserved over time. This is based on the First Law of Thermodynamics (conservation of energy) and Newton's Laws of Motion (conservation of momentum) respectively. Therefore, the relationship between a cause and its effect is best understood as the transfer of energy or momentum from one object to another.
In simple terms, the Law of Causality can be thought of as a chain reaction where an effect is tightly linked to a physical cause. The effect is inextricably linked to the cause because it is the necessary outcome. To be certain, nothing can occur without a precipitating cause, and a cause will always result in an effect.
Further, this chain is regarded as unbroken since the origin of the universe. Essentially, no effect is uncaused or self-caused. There is no material evidence to support an uncaused or self-caused effect.
The Law of Causality extends beyond the physical world to the non-physical world. In the field of Epistemology, the Law of Causality is expressed as causal determinism [REF-CAU02].
Causal determinism - the relationship between cause and effect - is regarded as the rationale upon which we formulate knowledge. In fact, many epistemologists claim that the Law of Causality is axiomatic because it is a self-evident truth and is irrefutable [REF-CAU03].
Given that the Law of Causality is self-evident and irrefutable, we must conclude that the creation of the universe had a first cause. This conclusion is inescapable.
Since we know something does not come from nothing, we further conclude that this first cause must have been external to or outside of nature. Therefore, we claim that the universe came about by a supernatural, transcendent first cause.
Resources:
Summary: The Law of Non-Contradiction states that a given object cannot be in two contradictory or opposing states at the same time.

On what basis do we draw sound conclusions? How do we compare good from bad, best from worst, and right from wrong as we navigate the challenges of life? Without a sense of truth, we lose our ability to weigh options when making sound decisions.
Western philosophy generally regards the Law of Non-Contradiction as a principal way of thinking. The notion of either/or logic makes sense. Westerners believe in an objective system of truth that is logically coherent.
Eastern philosophy, however, generally regards the Law of Non-Contradiction as non-sense. The notion of both/and logic makes better sense. Easterners believe in a subjective system of truth.
Many regard the Law of Non-Contradiction as merely a social convention or personal preference. While others such as post-modernists believe that we cannot trust our senses and language to fully understand truth and reality. Truth, if it does exist, is elusive.
Aristotle's Law of Non-Contradiction states that a given object cannot be in two contradictory or opposing states at the same time. Aristotle characterized non-contradiction as "one cannot say of something that is and that is not in the same respect and at the same time." For example, a car cannot be white and black at the same time. Either it is white or black at any given time.
The Law of Non-Contradiction is formally based on either/or logic. Either/or logic acknowledges the existence of contradictory and opposing states. Either an object is in state (S), or it is not (not-S).
This system of thought acknowledges that reality can be known through our human senses and articulated using language. We can know with some degree of confidence that an object is in one state or another by means of simple observation or testing. Statements identifying an object's state are either true or false.
Finally, this system of thought allows for both absolute and relative truths. Absolute truth is defined as an external, objective, and universal truth. Whereas relative truth is defined as an internal, subjective, and individual truth.
In summary, either/or logic acknowledges that truth is both exclusive and knowable.
The Law of Non-Contradiction has been challenged throughout the ages. One of the most influential objectors was German philosopher, G.W.F. Hegel in the mid-19th century [REF-DIA01]. He regarded the notion of truth based on either/or logic as fallacious.
Hegel created a system of thinking based on both/and logic known as dialectic logic. This system of thinking states that multiple conflicting truths could coexist in space and time. Therefore, an object can be in a state (S) and its opposing state (not-S) at the same time.
For Hegel and other proponents of both/and logic, there is no such thing as absolute truth. Hegel's system of logic is based on human perspective where truth is in the mind of the beholder.
Post-modernist John Caputo also claims that there is no such thing as absolute truth,
"The truth is that there is no objective truth about reality."
While Caputo's use of the word truth makes for an amusing rhetorical device, his statement is utterly self-refuting. How can Caputo claim for certain that there is no absolute truth when Post-modernists do not believe in a certain truth! When it comes to knowing truth, Post-modernists believe that the human senses, science, and mathematics cannot be trusted.
Post-modernists have systematically deconstructed the word truth so that it has been stripped of its intended meaning. It has come to mean perception or belief. This is what Stephen Colbert calls truthiness - the quality of seeming to be true but not necessarily or actually true according to known facts.
In summary, both/and logic acknowledges that truth is both non-exclusive and elusive.
The irrationality of both/and logic is best illustrated by Ravi Zacharias. Regarding the Law of Non-Contradiction and dialectic logic, Zacharias shares his encounter with an Eastern professor.
As the professor waxed eloquent and expounded on the law of non-contradiction, he eventually drew his conclusion: "This either/or logic is a Western way of looking at reality. The real problem is that you are seeing contradictions as a Westerner when you should be approaching it as an Easterner. The both/and is the Eastern way of viewing reality."
After he belabored these two ideas on either/or and both/and for some time, I finally asked if I could interrupt his unpunctuated train of thought and raise one question. I said, "Sir, are you telling me that when I am studying Hinduism I either use the both/and system of logic or nothing else?"
There was pin-drop silence for what seemed an eternity. I repeated my question: "Are you telling me that when I am studying Hinduism I either use the both/and logic or nothing else? Have I got that right?"
He threw his head back and said, "The either/or does seem to emerge, doesn’t it?"
"Indeed, it does emerge,"
I said. "And as a matter of fact, even in India we look both ways before we cross the street.
It is either the bus or me, not both of us."
The Law of Non-contradiction vs. The Dialectical System, [REF-ZAC02] [REF-ZAC03]
Because this Eastern professor disagreed with Zacharias, he really did believe in the Law of Non-Contradiction. He believed emphatically that the both/and system of thinking was the only valid way of thinking.
Jesus illustrated the consequences of both/and thinking when he made the following profound claim,
"I am the way, the truth, and the life. No one can come to the Father except through me." (John 14:6).
This claim clearly states that Jesus is the only way to the true God and that all other paths do not lead to God. If this claim is false, then Jesus was mistaken and there are other equally valid paths to God. However, if Jesus' claim is true, then all other religious systems of the world are false.
Based on the Law of Non-Contradiction and either/or logic, both interpretations of Jesus' claim cannot be true at the same time. The consequence of misinterpreting Jesus' claim about himself would lead to eternal separation from God. The ultimate question is whether Jesus was claiming an exclusive truth or not [BIB-IS14].
If it were not for the existence of absolute truth and the Law of Non-Contradiction, we would not be able to reason about anything. If all things are true, anarchy would ensue, and we would not survive as a human race.
Resources:
Argument:
(P1) The Universe had a Beginning [COS-IS01]
(P2) Everything that begins to exist has a cause [PHY-IS01]
(P3) Something Cannot Come from Nothing [PHY-IS02]
(C) Therefore, the Universe had a Transcendent First Cause
Our understanding of the origin and development of the universe has evolved over the millennia. Before the emergence of the physical sciences, many cosmologists believed that the earth was flat and the center of the universe.
Fortunately, scientific discoveries over the past two hundred years have produced an overwhelming amount of evidence dispelling previously held theories in cosmology. Specifically, this evidence points to a singular beginning of the universe.
The Kamal Cosmological Argument was espoused by Al-Ghazali. Al-Ghazali was a twelfth century Muslim theologian from Persia. He was concerned that Muslim philosophers of his day were being influenced by ancient Greek philosophy to deny God’s creation of the universe. After thoroughly studying the teachings of these philosophers, Ghazali wrote a critique of their views entitled The Incoherence of the Philosophers. He argued that the idea of a beginning less universe is absurd. The universe must have a beginning, and since nothing begins to exist without a cause, there must be a transcendent creator of the universe.
Conversely, Naturalists deny the existence of a transcendent first cause to explain the origin of the universe. They posit that even if a creative force were to exist, it would be within the system, not outside.
The American Humanist Association [REF-AHA01] argues that the universe is a self-existent closed system comprised of space, time, and matter which is uniformly held together from within. This implies the Law of Causality is an inexorable, unbreakable chain of causes and effects without beginning (self-existent) or end (eternal).
We know from modern science that this claim of a self-existent universe is false. Science has proven that the universe had a beginning [COS-IS01] and is progressing toward a final state of heat death [COS-EV06]. The universe is neither uniform nor cyclic.
Based on the Laws of Causality and Non-Contradiction, we know that SOMETHING cannot be created from NOTHING. Since the results of all natural events are the result of natural causes, the original cause of nature itself must been supernatural. Otherwise, nature would not have an origin, which has been proven scientifically as untrue.
Al-Ghazali referred to this supernatural cause as a transcendent cause. By transcendent he meant that the agent by which the universe was created was OUTSIDE the universe. This agent must be independent of space, matter, and time. We refer to this agent as supernatural because this agent is above or outside of nature.
According to Robert Jastrow, an agnostic astronomer at the Mount Wilson observatory,
"There are what I or anyone would call supernatural forces at work is now, I think, a scientifically proven fact." [REF-CTT01]
Jastrow concluded that the External First Cause cannot be explained naturally.
Likewise, Arthur Eddington one of Einstein’s contemporaries came to the same conclusion when he said,
"The beginning seems to present insuperable difficulties unless we agree to look on it as frankly supernatural". [REF-EDD03]
Many other secular scientists have come to the same conclusion.
From the Christian Evidences Series, R. C. Sproul argues that the only plausible and rational explanation for the existence of the universe is a self-existent eternal being [REF-RCS01]. He further argues that the other two popular explanations of a self-existent universe or a self-created universe violate the Laws of Causality and Non-Contradiction.
Sproul claims, the whole notion of self-creation is absurd in that the universe would have to exist before it existed in order to create itself.
Further, the notion of a self-existent, eternal universe, popular in the 1800's, has been proven by the scientific community in the last century as false.
Science demonstrated that the universe has a temporal beginning and the universe is finite, therefore must have been created by a transcendent, self-existent, eternal being or the Christian notion of God.
According to Paul in Romans 1:18-20 NLT , mankind has no excuses for his ignorance.
18 God shows his anger from heaven against all sinful, wicked people who suppress the truth by their wickedness. 19 They know the truth about God because he has made it obvious to them. 20 For ever since the world was created, people have seen the earth and sky. Through everything God made, they can clearly see his invisible qualities—his eternal power and divine nature. So, they have no excuse for not knowing God. (Romans 1:18-20)
Paul is saying that God's power and nature are "obvious" in creation. By using logical and empirical methods we can readily observe the transcendent, formative power of God. Modern science bears witness to this.
Resources:
Copyright@2025 Mainstream Apologetics